We analyze peer-reviewed research on supplements.
We rely on peer-reviewed scientific research to determine what’s truly effective. Our goal is to provide clear, unbiased information to help you make better health decisions.
We use AI tools to help summarize studies, and every piece of content is reviewed and approved by qualified experts, ensuring it’s accurate and trustworthy.
Beta Glucan is fully independent — we don’t sell products, run ads, or accept sponsorships. Our only focus is delivering reliable, science-backed insights.
Clinical studies have used varying doses of yeast-derived (1,3)-(1,6) β-glucan, and practitioners should use the most pure beta glucan available due to its superior biological activity:
- Children: 100 mg daily
- General Adult Use: 250–500 mg daily for ongoing immune support
- High-Stress Periods / Athletes: 250 mg daily
- Acute Symptom Support: Up to 900 mg daily during illness
- Vaccine Enhancement: Begin supplementation at least one week before vaccination and continue for 2–4 weeks after
Note: Take on an empty stomach for optimal absorption. β-glucan is recognized by immune cells in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (Peyer's patches) and transported to immune organs.
For comprehensive dosing guidance, see: Delivery Methods & Dosage
Download PDF Protocol
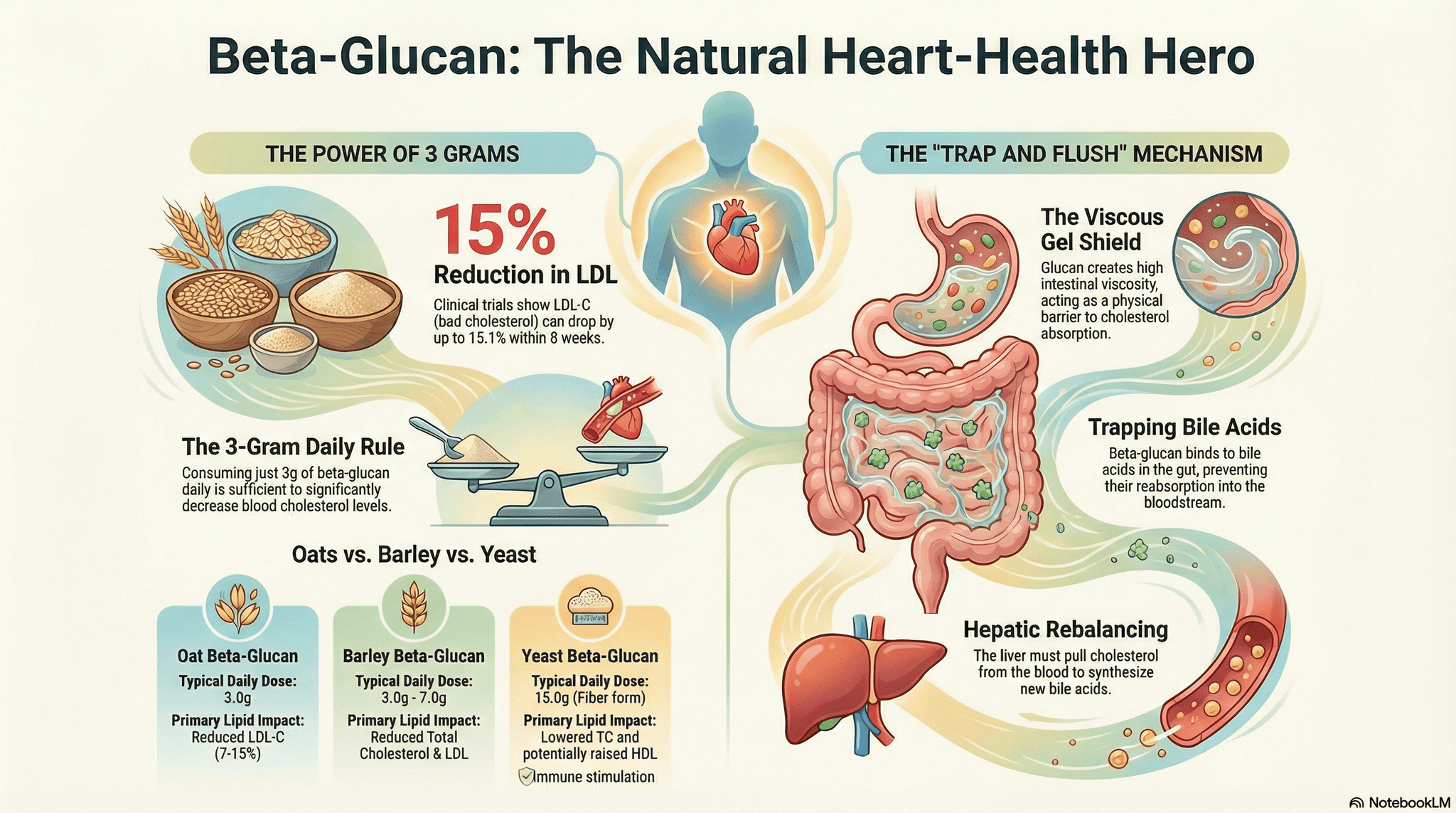
Download ProtocolEating oatmeal daily for 6 weeks improved “bad” cholesterol and was linked to helpful gut-bacteria changes.New
A higher-molecular-weight barley fiber (β-glucan) changed gut bacteria in ways linked to better heart health-associated markers.New
Barley fiber lowered cholesterol by boosting the body’s bile-acid production.New
Not all cereal fibers are equal: highland barley β-glucan most strongly improved “metabolic syndrome” features in mice and calmed liver-fat/inflammation pathwaysNew
A common immune-boosting sugar (β-glucan) protects liver immune cells in sepsis and helps clear bacteria in mice.New
Barley β-glucan reduced fatty liver and improved blood fats in mice fed a Western-style dietNew
Barley fiber changed liver and fat-tissue genes for fat handling and improved health markers in obese miceNew
A short, small study hints that two yeast-derived oat-like fibers (β-glucans) may reduce blood sugar, cholesterol, and inflammation markers in healthy middle-aged men.New
Barley-fiber–rich extracts eased “fatty-diet + stress” memory problems in mice by improving gut microbes, gut lining, and brain signals. New
Yeast Beta-Glucan Improves Metabolic and Inflammatory Markers in Obese Dogs with Insulin ResistanceNew
- Wouk β-Glucans as a panacea for a healthy heart? Their roles in preventing and treating cardiovascular diseases 2021
- Cicero A randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Medium-Term Effects of Oat Fibers on Human Health: The Beta-Glucan Effects on Lipid Profile, Glycemia and inTestinal Health (BELT) Study 2020
- Xu Serum Metabolomics Reveals Underlying Mechanisms of Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Oat Consumption: A Randomized Controlled Trial in a Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Population 2021
- Rioux-Labrecque Supplementation with a β-glucan tablet has no effect on hyperlipidemia: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial 2023
- Garcia-Cordero Dietary Supplements Containing Oat Beta-Glucan and/or Green Coffee (Poly)phenols Showed Limited Effect in Modulating Cardiometabolic Risk Biomarkers in Overweight/Obese Patients without a Lifestyle Intervention 2023
- Ferguson High molecular weight oat β-glucan enhances lipid-lowering effects of phytosterols. A randomised controlled trial 2020
- Morales Modulation of human intestinal microbiota in a clinical trial by consumption of a β-D-glucan-enriched extract obtained from Lentinula edodes 2021
- Reiners Effect of a regular consumption of traditional and roasted oat and barley flakes on blood lipids and glucose metabolism-A randomized crossover trial 2023
- Santisteban Efficacy of Food Industry By-Product β-Glucan/Chitin-Chitosan on Lipid Profile of Overweight and Obese Individuals: Sustainability and Nutraceuticals 2024
- Kang Barley-Based Cereals Enhance Metabolic Health and Satiety in Overweight Korean Adults: A Randomized Trial 2025
- Morias Junior The separate effects of whole oats and isolated beta-glucan on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials 2023
- Ferriera Metabolic variables of obese dogs with insulin resistance supplemented with yeast beta-glucan 2022
- Fan Barley polysaccharides modulate metabolic and mild cognitive impairment in naturally aging mice through the liver-gut-brain axis 2025
- Ikewaki Beta 1,3-1,6 Glucans Produced by Two Novel Strains of Aureobasidium Pullulans Exert Immune and Metabolic Beneficial Effects in Healthy Middle-aged Japanese Men: Results of an Exploratory Randomized Control Study 2023
- Mio Effects of β-glucan Rich Barley Flour on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in the Ileum, Liver, and Adipose Tissues of High-Fat Diet Induced-Obesity Model Male Mice Analyzed by DNA Microarray 2020
- Liu Hepatic Lipidomics Analysis Reveals the Ameliorative Effects of Highland Barley β-Glucan on Western Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Mice 2021
- Yang Effects of β-Glucan from Three Different Sources on Glucolipid Metabolism in Mice with Metabolic Syndrome 2025
- Wang Barley β-glucan reduces blood cholesterol levels via interrupting bile acid metabolism 2017
- Wang High Molecular Weight Barley β-Glucan Alters Gut Microbiota Toward Reduced Cardiovascular Disease Risk 2016
- Ye Oatmeal induced gut microbiota alteration and its relationship with improved lipid profiles: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial 2020