We analyze peer-reviewed research on supplements.
We rely on peer-reviewed scientific research to determine what’s truly effective. Our goal is to provide clear, unbiased information to help you make better health decisions.
We use AI tools to help summarize studies, and every piece of content is reviewed and approved by qualified experts, ensuring it’s accurate and trustworthy.
Beta Glucan is fully independent — we don’t sell products, run ads, or accept sponsorships. Our only focus is delivering reliable, science-backed insights.
Clinical studies have used varying doses of yeast-derived (1,3)-(1,6) β-glucan, and practitioners should use the most pure beta glucan available due to its superior biological activity:
- Children: 100 mg daily
- General Adult Use: 250–500 mg daily for ongoing immune support
- High-Stress Periods / Athletes: 250 mg daily
- Acute Symptom Support: Up to 900 mg daily during illness
- Vaccine Enhancement: Begin supplementation at least one week before vaccination and continue for 2–4 weeks after
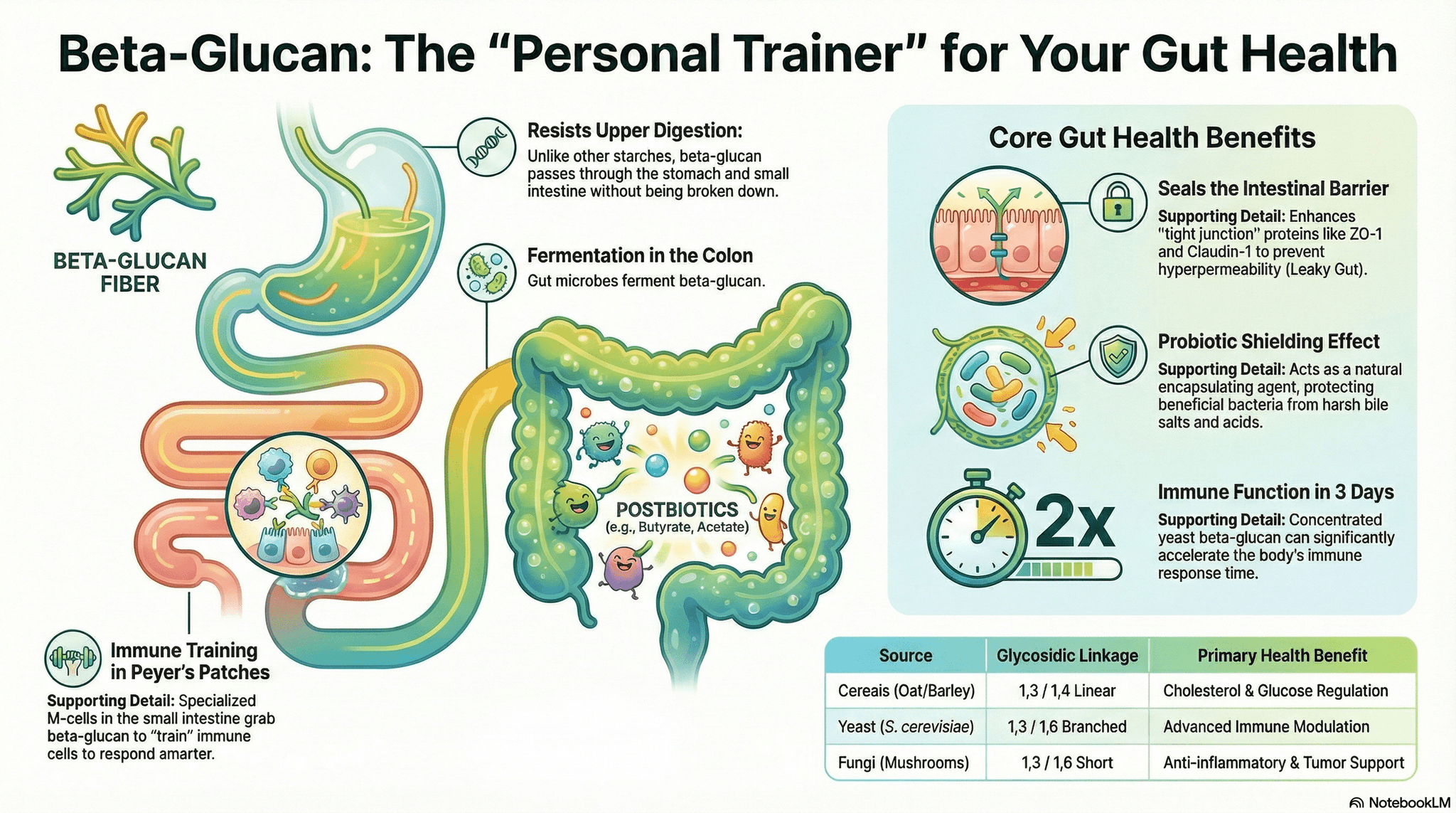
Note: Take on an empty stomach for optimal absorption. β-glucan is recognized by immune cells in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (Peyer's patches) and transported to immune organs.
For comprehensive dosing guidance, see: Delivery Methods & Dosage
Download PDF Protocol
Download ProtocolMushroom-derived β-glucan eased arthritis in mice by calming joint inflammation and nudging gut bacteria toward a healthier balance.New
A yeast fiber (β-glucan) trained gut immunity and gut bacteria and helped delay type 1 diabetes (T1D) progression in miceNew
Daily fiber drinks did not stop a painkiller-related “leaky gut” effect in older adults after 6 weeks. New
“Refined” lab diets sped up aging-like problems in mouse liver and brain; adding fiber slowed memory decline but didn’t fix liver issues. New
Barley-fiber–rich extracts eased “fatty-diet + stress” memory problems in mice by improving gut microbes, gut lining, and brain signals. New
Yeast fiber reshaped the gut, calmed brain inflammation, and eased Alzheimer-like changes in high-fat-fed rats. New
Yeast Beta-Glucans (β-glucans) incorporated in a Dry Food Diet may Boost Healthy Dogs' Gut Health and Immune ResponseNew
Natural Supplement May Help Gut Health in Children with AutismNew
Breathe Easy? Pleuran (Mushroom Extract from β-(1,3/1,6)-D-glucan) May Help Kids with AsthmaNew
A Daily Beta Glucan (β-glucan) Supplement May Boost Flu Shot Benefits in Older AdultsNew
- Morales Modulation of human intestinal microbiota in a clinical trial by consumption of a β-D-glucan-enriched extract obtained from Lentinula edodes 2021
- Singh β- glucans: a potential source for maintaining gut microbiota and the immune system 2023
- Cronin Yeast β-glucan supplementation lowers insulin resistance without altering microbiota composition compared with placebo in subjects with type II diabetes: a phase I exploratory study 2024
- Wang High Molecular Weight Barley β-Glucan Alters Gut Microbiota Toward Reduced Cardiovascular Disease Risk 2016
- Velikonja Alterations in gut microbiota composition and metabolic parameters after dietary intervention with barley beta glucans in patients with high risk for metabolic syndrome development 2019
- Korczak Effects of oats on gastrointestinal health as assessed by in vitro, animal, and human studies 2020
- Ye Oatmeal induced gut microbiota alteration and its relationship with improved lipid profiles: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial 2020
- Mall Effects of Dietary Fibres on Acute Indomethacin-Induced Intestinal Hyperpermeability in the Elderly: A Randomised Placebo Controlled Parallel Clinical Trial 2020
- Pihelgas The gut microbiota of healthy individuals remains resilient in response to the consumption of various dietary fibers 2024
- Han Research progress on natural β-glucan in intestinal diseases 2022
- Xu The Prebiotic Effects of Oats on Blood Lipids, Gut Microbiota, and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Subjects Compared With Rice: A Randomized, Controlled Trial 2021
- Raghavan Benefits of Gut Microbiota Reconstitution by Beta 1,3–1,6 Glucans in Subjects with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases 2022
- Marchi Effects of increasing levels of purified beta-1,3/1,6-glucans on the fecal microbiome, digestibility, and immunity variables of healthy adult dogs. 2024
- Mo Yeast β-glucan alleviates high-fat diet-induced Alzheimer's disease-like pathologies in rats via the gut-brain axis 2024
- Huang Oat β-glucan enhances gut barrier function and maintains intestinal homeostasis in naturally aging mice 2025
- Fan Barley polysaccharides modulate metabolic and mild cognitive impairment in naturally aging mice through the liver-gut-brain axis 2025
- Kromm Aging-related decline in the liver and brain is accelerated by refined diet consumption 2025
- Gudi Complex dietary polysaccharide modulates gut immune function and microbiota, and promotes protection from autoimmune diabetes 2019
- Zheng Polyporus Umbellatus polysaccharide ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis via inhibiting inflammation and regulating gut microbiota 2025
- He Deciphering immunoregulatory mechanisms and structure-guided biosynthesis of β-glucans 2025